
Be informed about the latest WP Cross-Site Request Forgery, identified and reported publicly. As these WP CSRF MAR 2024 vulnerabilities have a severe negative impact on any WordPress Security, consider our security audit. It is a -16% DECREASE compared to previous month, as specifically targeted Cross-Site Request Forgeries. Consider for your online safety, a managed WP/Woo Security AUDIT, – OR – switching with a TOP10LIST alternative WP Security Plugin - OR - Hire professionals for managed Security.
As these Cross-Site Request Forgeries cases from publicly reported vulnerable plugins are on your domain, it opens Pandora’s box from a security point of view. The following cases made headlines PUBLICLY just last month in the WP CSRF MAR 2024 & WP Cross-Site Request Forgery category:
| WordPress CSRF & Cross-Site Request Forgery reported in 2023: | 949 |
| WordPress CSRF & Cross-Site Request Forgery reported in 2024: | 103 |
BRIEF: WP Cross-Site Request Forgery is a type of malicious exploit of a website where unauthorised commands are submitted from a user that the web application trusts. Cross-site request forgery is also known as one-click attack, session riding, CSRF, XSRF, Sea Surf, Session Riding, Cross-Site Reference Forgery, or Hostile Linking. 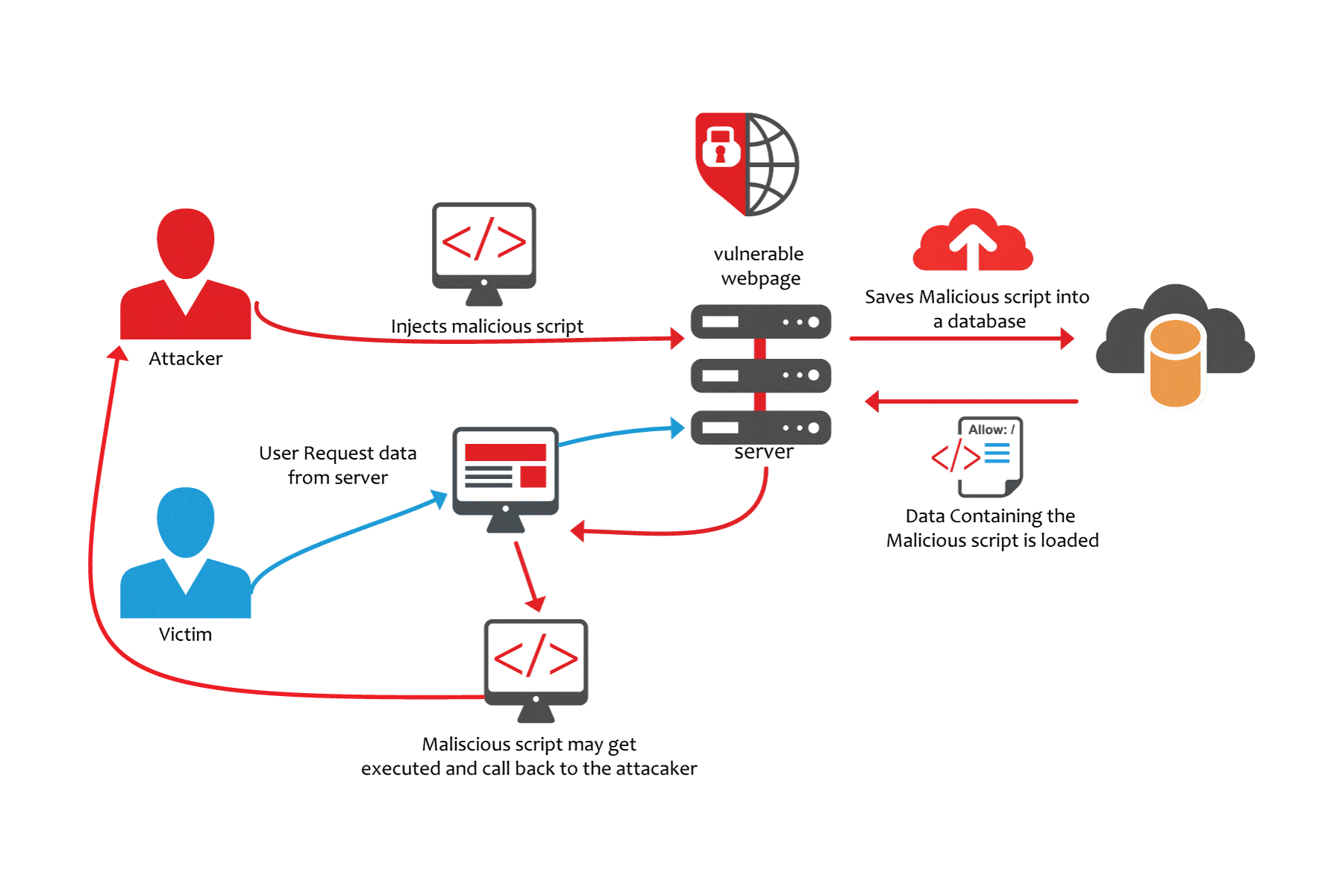
Cross-site request forgery (also known as CSRF) is a web Security vulnerability that allows an attacker to induce users to perform actions that they do not intend to perform. It allows an attacker to partly circumvent the same-origin policy, which is designed to prevent different websites from interfering with each other. Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is an attack that forces an end user to execute unwanted actions on a web application in which they’re currently authenticated. With a little help of social engineering (such as sending a link via email or chat), an attacker may trick the users of a web application into executing actions of the attacker’s choosing. If the victim is a normal user, a successful CSRF attack can force the user to perform state-changing requests like transferring funds, changing their email address, and so forth. If the victim is an administrative account, CSRF can compromise the entire web application.
In a successful CSRF attack, the attacker causes the victim user to act unintentionally. Example: this might be to change the email address on their account, to change their password, or to make a funds transfer. Depending on the nature of the action, the attacker might be able to gain full control over the user’s account. If the compromised user has a privileged role within the application, then the attacker might be able to take full control of all the application’s data and functionality.

How wonderful would be to simply let others take care of your chores? We absolutely understand why you would want that. This is why we propose this unique campaign: the price of a premium cup of coffee per week, for your first managed service.
Start simply by contacting us with your selections: